A "Hello
World" program is a simple program that will prints out a "Hello
World" text. It consists of the basic structure that every single program
needs for a programming language, therefore it's the best example to be used. Since on the last tutorial, I explained how to set up
Netbeans, a Java IDE, I'll be demonstrating the examples with the help of
Netbeans. If you're asking what is an IDE and why we need to use one, read this article to know about it.
Index for this tutorial:
Creating A New Project Folder
After the menu is
opened, you'll notice that there are many options available to create a new
project for Java application. We'll be creating a project folder with Maven
included. Maven is a build automation tool. A build tool helps us to develop an
executable application (.class file) from the source code (.java file) of the
application. While automating builds reduce the manual, annoying and
time-consuming work need to be done when programmers want to build
executables.
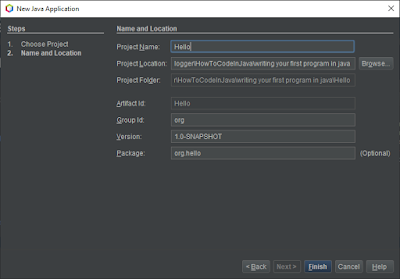
After you choose
"Java with Maven" in the left menu, now in the right list, select the
"Java application" option and click next. In this section, you can
specify the name and location to save the project folder. I'll name mine "HelloWorld". For the packaging
field, leave it as it is. Finally, you can click finish.
Creating a new file
When the project
folder is created, there won't be any files created beforehand for you, so
you'll need to create one yourself. First, you'll need to open the menu for
file creation, and there are couples of ways to this. You can do this by either
press "CTRL+N" or click the "file" icon at the toolbar
section. The third way will require longer time but knowing it might come in
handy one day. Now, navigate to the project file manager at the left-hand side
of the Netbeans window, navigate to your project folder and search for the folder that has the same name as the project folder. Now, right-click the folder and choose.
After you opened up the menu, choose "Java" in the left panel and "Java class" in the right panel, click next afterwards. Now give the file a name, any name will be just fine, I'll name mine as "HelloWorld". Lastly, click finish, and we have now added a new file to our project.
The Code
Code walkthrough
Every programming
language has its syntax when compiling a programmer's code. A programming
language syntax is a set of rules that defines the correct symbol's sequence
that's used to form a structured program correctly. It's just like English. It
has its own unique grammar rules as well as other languages in our world. For
us to communicate in English, we will need to follow those rules so that other
people can understand what we're saying. Now, let's walk through the code
together.
package org.helloworld;
Packages are a way for Java developer to organize
and group relate Java classes in multiple folders in a directory while providing
them to write maintainable code. When the size of an application becomes
bigger, programmers will sometimes forget the class names that they have used,
which would often lead to class naming conflict.
 |
| Photo by Wonderlane on Unsplash |
In Java, we cannot have two classes with the same name
in the same package. It'll cause an error during compilation. Therefore, by
using packages, a class with the same name but are from different packages would
not cause an error.
The package is the keyword to indicate
that this file belongs to a group/folder, while org.helloworld is
the name for the package. Keywords or reserved words are important in Java and
any other programming language. We cannot use any of them as a variable or
object name as they're reserved by Java.
public class HelloWorld {
This line of code declares a class called HelloWorld.
The public before the class keyword is an
access modifier, and access modifier specifies the visibility of a class
towards other class. So by making a class public means that
the class is visible to all other classes. I'll provide more information
regarding access modifier in another article. Every code in Java must be inside of a class, except for things like package declaration and libraries importing. This means that every file in Java will need at least one class in it.
The next keyword class is a general term or a
blueprint for an object. You can imagine an object as the things that are
present in our world, a Toyota car, for instance. A class or you can say a blueprint for an object can be used to make many other different objects, while every single one of them has their own unique properties.
For a longer explanation, let's use cars as our example. A car (represent a class) is the general
term for all cars. All cars use the very same basic blueprint for
their structure and have the same functionality, and that's transportation. A Mercedes car (represent an object or an instance of a class) is a car of a luxury's vehicle
brand. It uses the blueprint of a car for its structure. This also goes to the other car of the same brand and model. All of them are the same thing (built using the
same blueprint) except they come with different design
of their own (colour, spoiler, plate number and many more). Making every single one of them have their unique properties and
different from each other.
I hope that this example shows you the concept of class and object. If you're
still confused about this, please leave a message in the comment section below
and I'll try to re-explain it based on your understanding.
Now, for the open curly bracket, {, means
the beginning of a new block or a new scope. Whenever we create a new class,
method, conditional statement and loop, we will use a curly bracket to specify
the scope of the code and variable that belongs to block. While, the closing
curly bracket, }, indicate the end of a block. In our example, it's
used to define a new scope for our HelloWorld class. I will write an article
regarding scope soon, so don't worry.
public static void main (String[] args)
{
 |
| Photo by Christopher Robin Ebbinghaus on Unsplash |
Here, public means the same as the explanation I gave earlier, it's visible by all other classes, including the
Java runtime. If we provide the main method with a non-public access modifier, there
will be some restriction to the accessibility of the class and will cause an
error during compilation.
Static
Next, static is another common
keyword in Java. Explaining this would need another article, as there's a lot
of things that we need to know about the use of static in
Java. But, in our case, the static main method can be accessed
without the presence of an object. Since no object is
present during the runtime, therefore, the main method has to be static so
that the JVM can load the class into the main memory and
execute it.
Void
Java requires that all of its methods will need to
provide a return type. Our main method doesn't need to return anything;
therefore, its return type is a void type. More details regarding
the return type will be explained in the upcoming tutorial.
main
This is the name for the Java main method. It's fixed
and cannot be changed to any other name. Changing the name will cause an error
to occur.
A method
You must have been wondering what does a method means,
as I have mentioned it in the previous sections. A method is a block/section of
reusable code. We can use back the block of code as many times we need and whenever
we need it. More information regarding method can be found here.
(String[] args)
This is the parameter for our main
method, with String as its type. As it's the parameter for
the main method, the value passed to it is called the command line
arguments. The arguments are taken when the programmers
specify some data during the compilation process. I'll write a tutorial on
how to include arguments during Java program compilation in Window's Command-Line Interface (CLI).
In short, Arguments is the values
that we want to pass to a method and parameters are the variable
defined in the method definition. If you don't know what's a variable, don't
panic as I'll cover it on the next tutorial. For simple explanation, think of
it as aa temporary way to store data when the program is running. Regarding why
we need parameters for a method will be explained in another article.
Also, another important thing is that whenever we specify a parameter
for a method, we need to enclose them in parentheses, ().
System.out.println("Hello
World");
Now for the final line, The System is
the name of a class that handles standard input, output, and error output
stream. While, out is one of the fields (class variable) in the System
class, it is defined as with the datatype PrintStream. While println is
a method inside of the PrintStream class. This method passes the arguments
specified in it to the standard console and printing out the arguments to the
console while adding a new line at the end of the output. In our case, the console
will print out a text "Hello World". There will be an article that
will cover on outputting things to the console.
Lastly, the semicolon (;), indicates the end of a
statement. Every single statement that you've written in Java will need to have
a semicolon at their end. We need to do it add it because it's to separate the
current statement with the next statement in the source code parsing phase
during the compilation process.
Running the file.
Now that we've gone through the code, it's time for us to run our program. Since we're using Netbeans running the Java file is easy, just press "shift+F6" and Java will start to compile the source code, and you will see the result of the code in the console that popped up. To compile a Java file through the command line, please refer to this tutorial.
That's it for this tutorial, and I hope you now
understand how the basic structure of a Java program works. If you find this
tutorial helpful remember to share it with other people that might be
interested in this topic. As always, if you have any suggestion, critics,
question, or mistakes regarding this tutorial, feel free to leave a comment
below. I'll try my best to reply to your comments. The next tutorial will be
"What is a variable in Java", so stay tuned.










No comments:
Post a Comment